In the world of electrical wiring and installations, choosing the right components is crucial to ensure both safety and performance. DIN Rail mounted terminal blocks are one of the essential elements used in various electrical applications. This guide will walk you through the factors you need to consider when selecting the right terminal blocks for your electrical needs.
Table of Contents
What Are DIN Rail Mounted Terminal Blocks?
DIN Rail mounted terminal blocks are used to connect electrical circuits and provide a secure and organized way to manage wiring. These terminal blocks are typically mounted on a DIN rail (a standardized metal rail), making them easy to install, maintain, and upgrade. Whether you are working with low voltage systems or high power installations, selecting the right terminal block ensures proper current handling and safety.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing DIN Rail Terminal Blocks
1.Current and Voltage Ratings
Each terminal block is designed to handle specific amounts of current and voltage. It’s important to choose one that matches or exceeds the electrical specifications of the system you are working with. Overloading the terminal block can cause overheating, system failure, or even fire hazards. Be sure to review the manufacturer’s datasheets for accurate rating information.
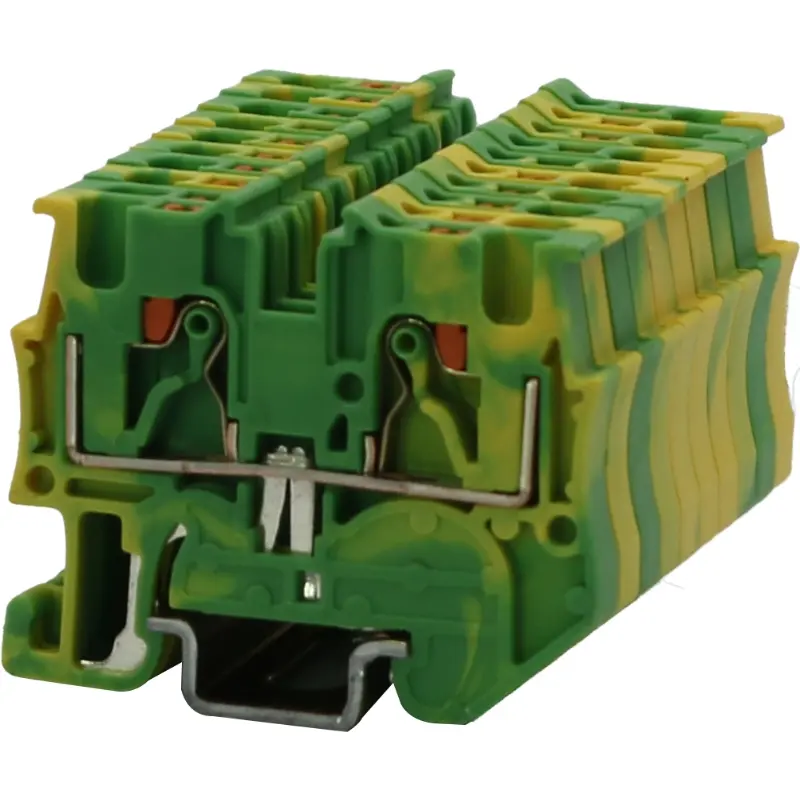

2.Material of Construction
Terminal blocks are made from various materials, each offering different advantages. Common materials include:
Polyamide (PA): Often used for general-purpose applications due to its durability and resistance to high temperatures.
Polycarbonate (PC): A high-strength material ideal for environments with higher mechanical stress.
Brass or Copper: Used for electrical conductivity, especially in high-power applications.
The material choice should align with the specific environmental conditions, including temperature, humidity, and mechanical stress, in which the terminal block will be used.
3.Size and Mounting Type
DIN Rail terminal blocks come in a variety of sizes. The size will depend on your electrical system’s wiring requirements. Terminal blocks must fit securely onto the DIN rail, which is typically available in three standard sizes: 35mm, 15mm, and 7.5mm.
When selecting the right size, consider the space available in your panel and how much wiring needs to be connected. Also, consider whether you need screw-type or spring-type terminals, depending on the ease of installation and maintenance.
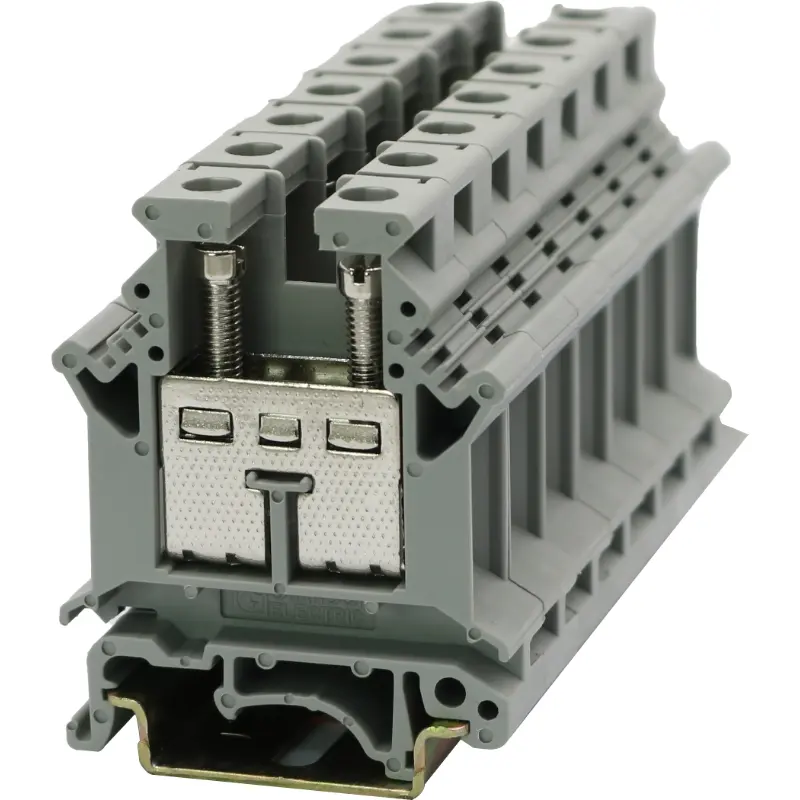
4.Safety Features
The safety of your electrical installation is paramount. Look for terminal blocks with additional safety features such as:
Insulated covers to protect users from accidental electrical contact.
Screwless connections for quick and reliable installation without the risk of improper tightening.
Locking mechanisms to prevent accidental disconnection during maintenance.
5.Environmental Conditions
Each terminal block is designed to handle specific amounts of current and voltage. It’s important to choose one that matches or exceeds the electrical specifications of the system you are working with. Overloading the terminal block can cause overheating, system failure, or even fire hazards. Be sure to review the manufacturer’s datasheets for accurate rating information.
6.Ease of Use and Installation
Choose terminal blocks that are easy to install and maintain. Look for options with clear labeling and color coding to reduce wiring mistakes. Some terminal blocks feature a modular design, allowing for easy expansion of wiring configurations.
7.Connection Types
The method of connecting wires to terminal blocks can vary, affecting installation speed and reliability.
Screw Terminals: Provide solid, secure connections but require a screwdriver for installation.
Spring Clamp Terminals: Allow for quick, tool-less connections; great for applications requiring frequent changes.
Push-in Terminals: Simplify the connection process—just push the wire into place.
Pros and Cons:
Screw Terminals: More reliable but slower to install.
Spring Clamp: Fast installation, but may not hold as securely under heavy vibration.
8.Additional Features
Look for terminal blocks that offer features enhancing usability and functionality.
Test Points: Some terminal blocks include test points for easy circuit testing without disconnecting wires.
Labeling Options: Choose blocks that allow you to label terminals clearly, which is especially helpful in complex installations.
9.Cost Considerations
While budget shouldn’t be the only consideration, it’s important to find terminal blocks that offer good value for money.
Compare Options: Look at different manufacturers and models to find a balance between cost and quality.
Long-Term Investment: Sometimes spending a little more upfront can save costs in the long run by reducing maintenance and replacement needs.
Why the Right Terminal Block Matters
Choosing the right terminal block ensures:
Reliable connections: Prevents loose connections that can cause sparks, overheating, or failure.
Safety: Correctly rated terminal blocks help prevent overloads, electric shocks, and potential fires.
Durability: The right material and design can extend the lifespan of your installation, reducing the need for maintenance or replacements.
Conclusion
Selecting the right DIN Rail mounted terminal block is essential for the success and safety of your electrical installations. By considering factors such as current rating, material, size, and environmental conditions, you can make informed decisions that will lead to reliable, safe, and efficient electrical systems. Whether you’re an electrical engineer or a DIY enthusiast, always ensure your terminal blocks meet the necessary requirements for your specific application.
Interested in learning more or need help selecting the right terminal block? Contact Gkoncy for expert guidance and discover our wide range of products tailored to your electrical needs!
